Sophos Firewall v22: Overview and all the new features
Sophos Firewall v22 focuses on hardening, clear visibility and stable operating processes. The modernized Xstream architecture, a hardened kernel and new operating functions help to reduce attack surfaces and simplify administration. This article explains all the new features of SFOS v22.
Topics
Health Check
The Health Check is the integrated configuration check in Sophos Firewall v22. The aim is to make misconfigurations visible at an early stage before they become a security or operational problem. It addresses the growing threat situation for Internet-exposed infrastructure and follows the secure-by-design approach according to CISA guidelines. Sophos has hardened the firewall over several releases, simplified patching and improved detection under attack. Unique features include over-the-air hotfixes without downtime and active monitoring of the installed base by Sophos to detect early indicators of attack.
What the Health Check is for
It evaluates dozens of settings against CIS benchmarks and established best practices. Typical check areas include outdated or insecure TLS ciphers, overly broad admin and user policies, unused or overlapping rules, unnecessarily exposed services, and baseline hardening such as time, authentication and logging. Sophos Firewall v22 makes it easier to keep policy hygiene high and eliminate unwanted vulnerabilities.
How the health check works
A dashboard widget in the Control Center shows the status. Click to access the detailed view or via the main menu under “Firewall health check”. Findings are prioritized, explained and linked with a drill-down to the appropriate settings screen. This allows deviations to be rectified without searching.
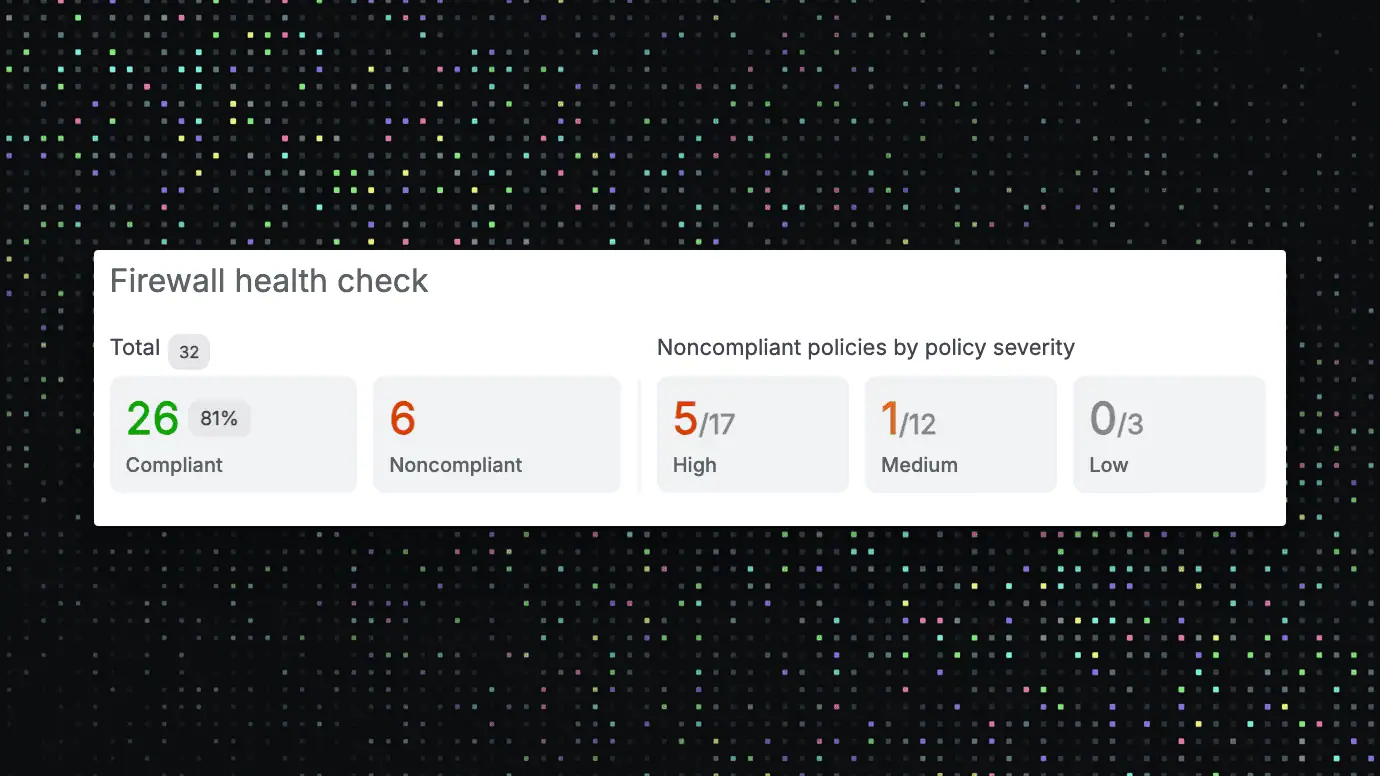
How to use the health check in operation
Before go-lives, after policy changes, after firmware updates and on a regular basis. It serves as an objective validation in CAB processes and provides audit evidence of ongoing policy hygiene.
The health check covers the configuration quality, not the hardware health. It does not check whether internal databases are consistent or whether RAM or SSD have write errors. A visible status display in the GUI would also be helpful here.
Health Check: test areas in detail
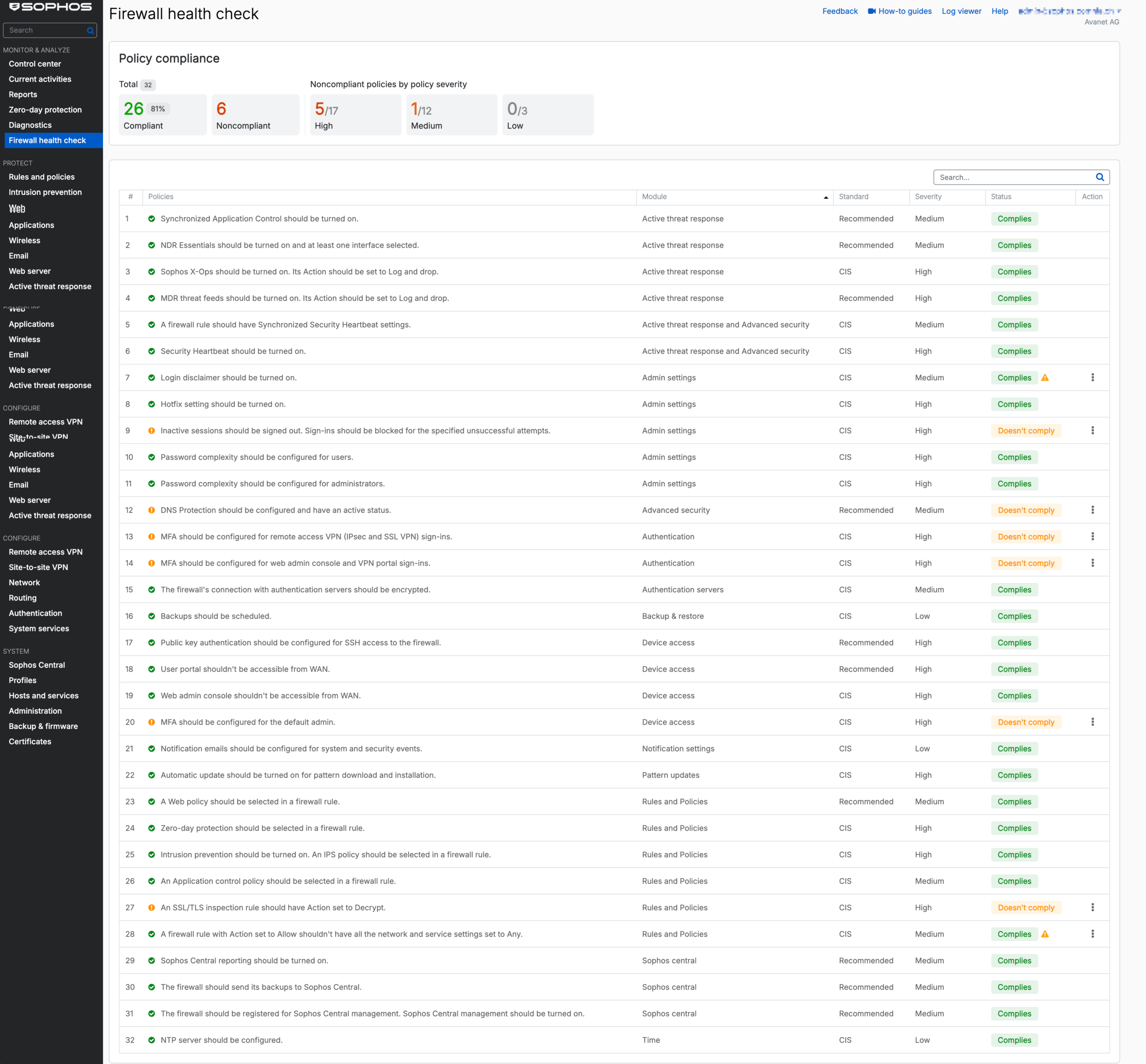
The health check lists all checked points in the dashboard, similar to a security audit. Each point shows the module, standard, severity, status and a direct action. This allows you to see at a glance which configurations deviate from best practice. A selection of the most important checks:
- Synchronized Application Control should be turned on.
- NDR Essentials should be turned on and at least on one interface selected.
- Sophos X-Ops should be turned on. An Action should be set to Log and drop.
- MDR threat feeds should be turned on. An Action should be set to Log and drop.
- A firewall rule should have Synchronized Security Heartbeat settings.
- Security Heartbeat should be turned on.
- Login disclaimer should be turned on.
- Hotfix settings should be turned on.
- Remote sessions should be signed out. Sign-ins should be blocked for the specified unsuccessful attempts.
- Password complexity should be configured for users.
- Password complexity should be configured for administrators.
- DNS Protection should be configured and have an active status.
- MFA should be configured for remote access VPN (IPsec and SSL VPN) sign-ins.
- MFA should be configured for web admin console and VPN Portal sign-ins.
- The firewall’s connection with authentication servers should be encrypted.
- Backups should be scheduled.
- Public key authentication should be configured for SSH access to the firewall.
- User portal shouldn’t be accessible from WAN.
- Web admin console shouldn’t be accessible from WAN.
- MFA should be configured for the default admin.
- Notification emails should be configured for system and security events.
- Automatic update should be turned on for pattern download and installation.
- A Web policy should be selected in a firewall rule.
- Zero-Day Protection should be selected in a firewall rule.
- Intrusion prevention should be turned on. An IPS policy should be selected in a firewall rule.
- An Application control policy should be selected in a firewall rule.
- An SSL/TLS inspection rule should have Action set to Decrypt.
- A firewall rule with Action set to Allow shouldn’t have all the network and service settings set to Any.
- Sophos Central reporting should be turned on.
- The firewall should send its backups to Sophos Central.
- The firewall should be registered for Sophos Central management. Sophos Central management should be turned on.
- NTP server should be configured.
This list shows that the Health Check covers both technical configurations and organizational security guidelines.
Some points make sense without question, others can be questioned. For example: “Login disclaimer should be turned on”. Such a disclaimer only increases security to a limited extent – nobody really reads it, and in practice it is usually simply clicked away. However, it fulfills legal requirements in certain environments, for example as a terms of use or disclaimer. In purely security terms, it is hardly a protective mechanism, but rather a formal point intended to signal security awareness.
You can manually overwrite the status of individual checks. This allows an item to be marked as “Complies”, even if it is not technically fulfilled. However, a ⚠️ symbol then appears to indicate the overwritten status. This ensures transparency while retaining administrative freedom.
It is also noticeable that some checkpoints have strong links to Sophos Central, MDR, NDR or DNS Protection. From Sophos’s point of view, this is of course also a form of cross-selling, as it emphasizes the benefits of its own ecosystem integration. Nevertheless, many of these recommendations provide real added value, for example through consolidated management or automated alerting.
Next-Gen Xstream Control Plane
With Sophos Firewall v22, Sophos has fundamentally evolved the Xstream Architecture. While the original concept was introduced in version 18 to fully exploit the performance of the XGS hardware, the new generation is aimed at much more than just performance: security, stability and future viability are the focus.
A new foundation for security and scalability
The revised Control Plane has been completely redesigned. Instead of a monolithic system, Sophos now relies on a modular framework in which central services such as IPS, web filtering or SSL inspection run in isolation from each other. Each service is like a separate app within the firewall and can be managed or restarted independently. This means that other functions remain stable even if a module reacts incorrectly or crashes.
From a security engineer’s perspective, this is a crucial step: this architecture minimizes dependencies and reduces the impact of potential exploits on individual components. At the same time, it creates the basis for zero-trust isolation within the system – a concept that was previously more familiar from modern cloud platforms.
Independent of hardware and environment
A major advantage of the new Xstream architecture is its complete independence from proprietary hardware. Unlike many of its competitors, Sophos Firewall v22 is not based on special ASICs or fixed-function chips. The architecture runs consistently on physical hardware, virtual machines or cloud environments. This ensures uniform behavior across all platforms and facilitates automation in operation.
Improved high availability with self-healing
Another new feature is the new self-healing logic in HA clusters. The control plane continuously monitors the status of both systems and automatically corrects deviations. If differences in the configuration or sync status are detected, the firewall automatically initiates a correction. This reduces error situations, lowers maintenance costs and noticeably improves availability. In practice, this means fewer unplanned restarts and more stable cluster performance.
Technical perspective and future
The new Xstream architecture lays the foundation for future features such as n-node clustering, fully containerized security services and a fully-fledged REST API for remote management and automation. Sophos Firewall v22 is thus clearly moving towards a platform architecture that is reminiscent of modern cloud principles – service-based, dynamic and security-centric.
From a professional point of view, this upgrade is more than just a technical update. It is changing the way firewalls will be designed in the future. Away from monolithic appliances and towards a flexible, service-oriented infrastructure that can be adapted quickly and managed automatically. For operators with high demands on uptime, compliance and scalability, this is a decisive step forward.
I completely agree – the reorientation towards CPU-based processing makes perfect technical sense. Not all XGS appliances have an NPU, which has accelerated traffic, and virtual firewalls in particular have always been at a disadvantage here. With the new architecture, performance is being shifted back to modern CPUs, which ensures uniform behavior across all platforms. In the older XGS desktop models, the combination of CPU and NPU was also thermally demanding, which led to higher noise levels. The new generations are significantly quieter thanks to the elimination of this dual processor load. Anyone who remembers the comparison will understand why the move back to CPU optimization makes strategic and practical sense.
Hardened kernel 6.6+
Sophos Firewall v22 uses a modernized Linux kernel (v6.6+) for increased security, performance and scalability. Key aspects are stricter process isolation and comprehensive mitigations against side-channel attacks and CPU vulnerabilities such as Spectre, Meltdown, L1TF, MDS, Retbleed, ZenBleed and Downfall. Additionally active are hardened usercopy, stack canaries and Kernel Address Space Layout Randomization (KASLR). This reduces the exploitability of memory errors, stabilizes the runtime behaviour and strengthens the foundation of the Xstream architecture.
Remote Integrity Monitoring
Remote Integrity Monitoring in SFOS v22 complements the hardening of the kernel by continuously monitoring system integrity. Simply put, it checks in the background whether something changes on the firewall that should not be there. The built-in Linux sensor for XDR registers security-relevant events at system and service level – for example, when a process starts that is not known, when configuration files are changed or rules are exported, or when critical files are manipulated.
This information is sent to Sophos Central together with the time, user and source. There it can be linked with other data – for example from endpoints, email gateways or identity services. This enables administrators to detect unusual behavior more quickly and react in a targeted manner before it becomes a major problem.
For the everyday life of an IT administrator, this means that if someone tries to change something on the firewall or manipulate a file without being noticed, this is detected and reported. The function therefore helps to detect silent attacks or misconfigurations at an early stage without having to constantly check manually. At the same time, it helps Sophos to centrally monitor the behavior of installed firewalls and thus identify patterns or potential security problems.
Active Threat Response (threat feeds for WAF and NAT) and
Under feature request SFSW-I-2618, a behavior that has been desired for a long time has finally been implemented. Threat feeds are dynamic lists of known malicious IP addresses that are continuously updated by threat intelligence providers like us(Avanet Threat Feeds). They are used to proactively block attacks from the Internet before they even get close to a service.
Until now, however, these feeds have only been used to protect Sophos portals. NAT and WAF rules remained unaffected – which, from a practical point of view, looked less like a missing feature and more like a bug.
With Sophos Firewall v22, this limitation has now been removed. Threat feeds are now also automatically applied to NAT and WAF rules. This means that as soon as a connection from an IP address is detected from a feed, the firewall automatically blocks it – even with forwarding or web server rules. You therefore no longer need to maintain separate rules or workarounds.
This change is a major step forward because the threat feeds now also protect productive services such as web servers and thus contribute directly to attack detection and defense. The firewall reacts to current threats in real time without the need for manual intervention. A small but technically significant detail that once again clearly increases the security value of Sophos Firewall v22.
NDR improvements
For outbound traffic, source IP matches with NDR Essentials and external feeds are supported to identify and block compromised, unmanaged devices. The NDR Essentials Threat Score appears directly in the logs. In addition, since SFOS v21.5 MR1, the region of the NDR Essentials Data Center can be explicitly selected; by default, the region with the lowest latency is used.
API Access Control
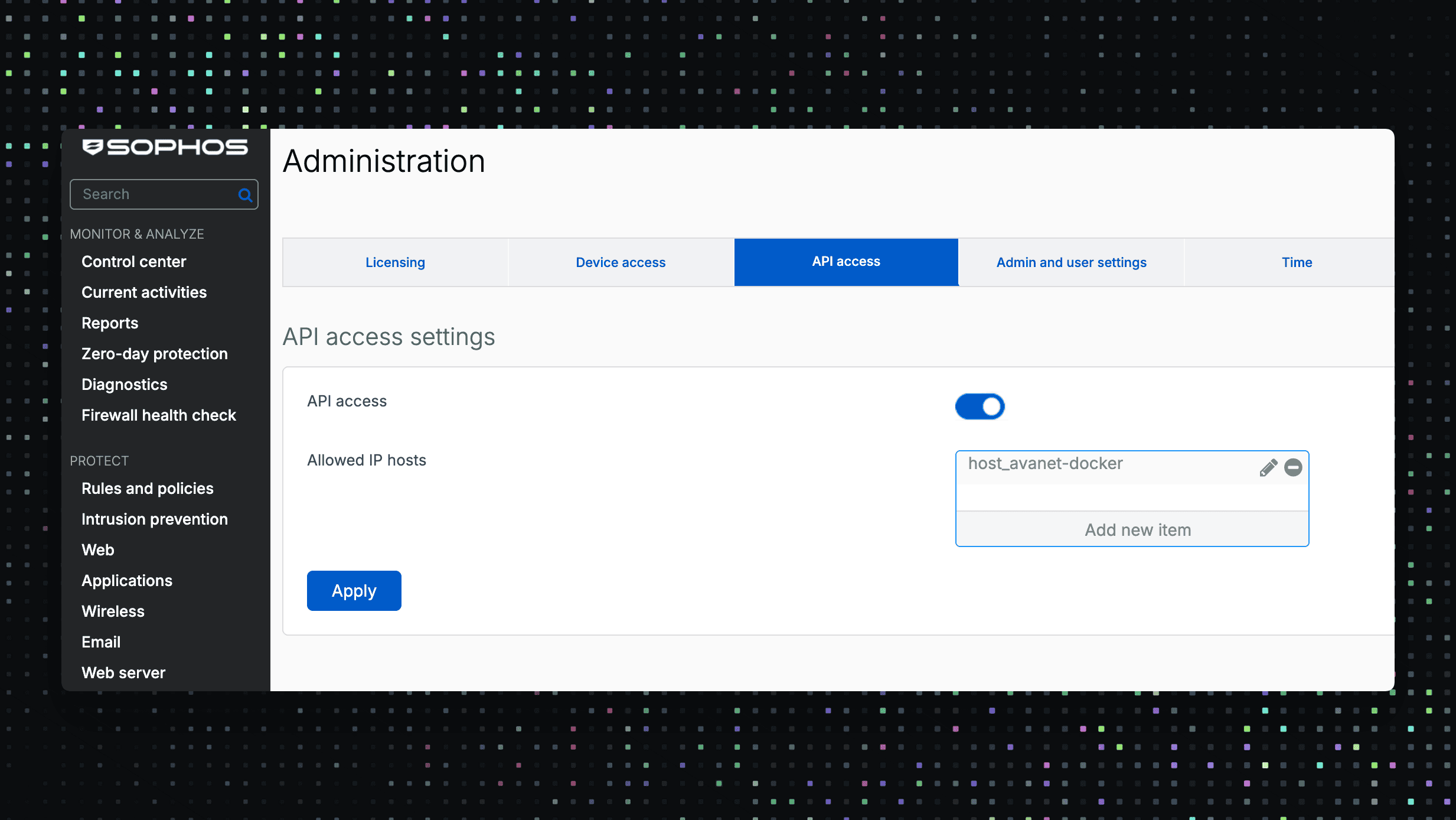
Access to the management API can be restricted to explicit IP objects. Up to 64 entries allow a clean separation between automation workers, management networks and external partner access. Change windows can be temporarily expanded and then reduced again. Recommendation: Only allow access from dedicated management networks, activate logging, check access regularly. Configuration takes place in SFOS v22 under Administration.
Firmware updates via SSL with certificate pinning
SFOS v22 validates update servers via SSL and certificate pinning. This reduces the risk of manipulated update infrastructure. In environments with strict egress policies, the target FQDNs should be included in allowlists so that updates work reliably.
HTTP/2 and TLS 1.3 for device access
The Web Admin Console, the VPN Portal and the User Portal now use HTTP/2 and TLS 1.3. These two technologies ensure that connections are established faster, are more stable and are better encrypted. The difference is particularly noticeable when logging in and accessing pages in the Web Admin interface, which react noticeably faster.
HTTP/2 bundles several requests into one connection, which means that the firewall has less waiting time between client and server. TLS 1.3 also ensures modern encryption with a shorter handshake and higher security. In older network environments where old firewalls or proxy systems are still in use, you should briefly check whether everything is compatible before activation.
Monitoring with sFlow and SNMP hardware values
sFlow enables traffic sampling to central collectors to detect volume peaks, unexpected flows and anomalies in real time. Default sampling rate is 400, minimum 10. Up to 5 collectors are supported. sFlow can be activated on physical interfaces, alias and VLAN interfaces. Note: FastPath is deactivated on the monitoring interface. In addition, SFOS v22 provides SNMP hardware metrics such as CPU and NPU temperature, fan speeds, power supply status from XGS 2100 and PoE performance values for all XGS models with PoE, except XGS 116(w). An MIB file can be downloaded directly in the UI. Select sampling and polling intervals so that core links remain visible without overloading the collector.
Better operation and search functions
With SFOS v22, the user interface should respond much faster. When switching between menus and tabs, you no longer have to wait until the page has completely reloaded.
No improvement was noticeable in my tests. Nevertheless, it is pleasing to see that work is being done on the speed of the user interface. There is still a lot of potential here, especially when saving firewall rules or loading the interface views, where there are still noticeable delays.
XFRM interfaces can now be filtered and searched directly in the interface. If there are many entries, they are automatically divided into pages, which significantly improves the overview and management of large IPsec setups.
Smaller improvements are also noticeable in everyday use: The NTP server settings are now set to “Use pre-defined NTP server” by default.
UTM related functions in SFOS
For all those who have not yet switched from SG UTM to SFOS, version 22 brings a missing feature. These include MFA support in the WAF, modern OTP algorithms such as SHA-256 and SHA-512 as well as audit trail logs with before/after display. These enhancements close important gaps compared to the previous UTM and make the changeover much easier. Anyone still hesitating to migrate will now find almost all the familiar features in SFOS v22 – with modern technology and better integration.
Audit trail logs in detail
Phase 1 records every change to firewall rules, objects and interfaces. The logs can be downloaded in the Diagnostics > Logs menu and clearly show exactly what has been changed – including the values before and after the adjustment. In future versions, these changes will be displayed directly in the Log Viewer so that differences can be seen immediately without exporting. This facilitates traceability and saves time when analyzing changes.
Instant Web Category Alerts
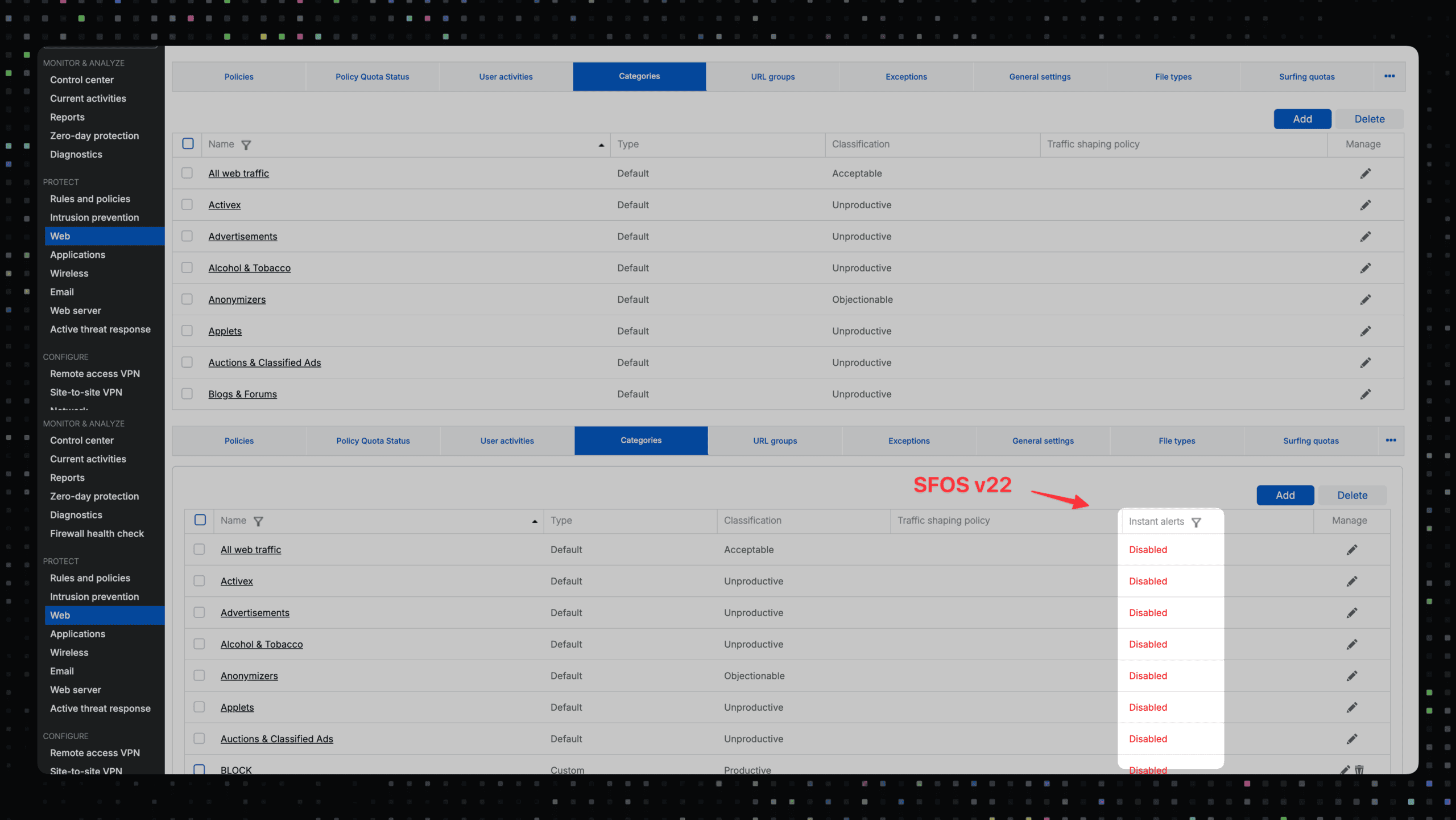
Automatic notifications can be set up for restricted web categories. These messages inform you at short intervals, for example every five minutes, about attempts to access blocked websites. Each message contains details such as time, user, category and domain accessed. This ensures greater transparency and makes it easier to track repeated access to unauthorized sites. This function is particularly helpful in environments with clear guidelines, such as schools or organizations with fixed Internet rules. Violations are automatically documented and can be traced if necessary.
Upgrade to SFOS v22: Paths, duration and notes
SFOS v22 brings profound changes to the system architecture. The firmware requires a little more storage space in the root partition. For most devices (around 98%), the upgrade runs automatically and without intervention. Models from XGS 2100 already have enough memory and update directly.
For XGS desktop and virtual models with a smaller partition (1 GB), the memory is automatically increased during the upgrade. This means that the process takes a little longer, usually between two and ten minutes. Only a few systems – around three percent – require manual preparation, such as deleting old reports or logs, in order to create sufficient space.
Devices with older SSD firmware must first be updated before the upgrade to version 22 is possible. Very old virtual installations that are still based on small hard disks or older SFOS versions (before version 18) require additional steps. In some cases, an interim update to version 21 MR2 is necessary before the upgrade can be successful. If the data carrier is too small, the only option is a new installation with a larger hard disk.
Instructions for all necessary steps appear automatically in the Firewall interface via messages in the Control Center, by email and through warning icons in Sophos Central. These also display a reference code that links directly to the relevant knowledge base article. After successful preparation, the warning disappears within about an hour. Additional CLI commands are also available for diagnostic purposes.
Conclusion
Sophos Firewall v22 impresses with a noticeably stronger security base, modular structure and more stable operation. The Health Check is a sophisticated tool that helps to systematically check configurations and adhere to best practices. The new Control Plane ensures smoother upgrades and greater reliability during operation. Modern protocols and extended telemetry make analysis and troubleshooting much more efficient.
We are pleased with the clear progress of Sophos Firewall v22, but we would still like to see work done on cloning and grouping NAT rules, as we are used to with firewall rules. About a year ago, we collected and published our wishes. A lot has improved since then, but we still feel that some functions are missing. We hope that they will be implemented in future versions.
FAQ
When will Sophos Firewall v22 be available as GA?
The early access phase started in October 2025 and Sophos usually releases the GA version a few weeks after the EAP. Based on previous release cycles, the GA release is expected in early December 2025.
What is the new Health Check and what is it used for?
The Health Check checks the firewall configuration for vulnerabilities and deviations from best practices. It evaluates settings such as TLS encryption, password complexity, MFA, admin access or update status and displays them clearly in the dashboard. The aim is to detect and rectify misconfigurations at an early stage before they become security problems.
What has changed in the Xstream Architecture?
The Xstream Control Plane has been completely rebuilt. Central services such as IPS or web filters now run in isolation from each other. This increases stability, as a faulty module no longer has an impact on other areas. At the same time, the architecture creates the basis for container services, API control and future scaling functions.
Why is CPU-based processing now better than the NPU solution of the older XGS series?
Not all firewalls have a dedicated NPU. The new CPU-oriented architecture ensures consistent performance across all platforms – even with virtual or cloud installations. In addition, the elimination of the NPU reduces heat development and thus the background noise, especially in smaller models.
What are the advantages of the new kernel (version 6.6+)?
The updated Linux kernel in Sophos Firewall v22 offers improved security mechanisms against attacks such as Spectre, Meltdown and Retbleed. It provides better protection against memory errors and stabilizes operation with additional protection mechanisms such as Stack Canaries and KASLR.
What’s new with Threat Feeds?
Threat feeds are now also applied to NAT and WAF rules. This means that the firewall automatically blocks known attacker IPs even before they reach an internal service. This function significantly increases the level of protection as it includes productive servers and redirects.
How does the upgrade to SFOS v22 work?
The upgrade takes place automatically on around 98% of devices. Systems with a small root partition (1 GB) expand this automatically during the process, which can take a few minutes longer. Only older installations or devices with outdated SSD firmware require manual preparation. All steps are clearly displayed via the GUI or by e-mail.
Are there any new monitoring functions?
Yes, in addition to SNMP hardware values (temperature, fans, power supplies, PoE), Sophos Firewall v22 now also supports sFlow for real-time traffic analysis. This allows unusual data flows or load peaks to be detected immediately.
Further links
- Avanet: Threat Intelligence Feeds for Sophos Firewall
- Sophos News: Sophos Firewall v22 Early Access
- Sophos Community: SFOS v22 EAP announcements
Sources
- Sophos Firewall OS v22 Key New Features
- Sophos Firewall v22 is now available in early access, Sophos News
- Sophos Firewall v22 EAP is Now Available, Sophos Community, 15.10.2025,




