Sophos Firewall v20 – Best features in new SFOS release
The major releases are by far the most exciting of the year and with Sophos Firewall v20, or more specifically SFOS v20, Sophos brings some really great new features. At the moment it is the EAP1, which is an Early Access version. The final version is not expected to be released until late this year or early 2024 if Sophos stays true to its scheme.
Sophos Firewall v20 Features
Web Admin optimized for 1920p
In Sophos’s feature list, this new addition is at the bottom of the less important improvements included in the new version. Support for high-resolution screens. Statista’s figures show that 1980p monitors have already been more than standard since 2018 – so this feature is long overdue. I’m extremely celebrating this feature. 🥳 It was extremely annoying that so much white space was left unused and text was cut off instead.
However, not everything is optimized for 1920p yet and many places in the GUI still need some maintenance, e.g. in the dashboard. But this should be delivered with v20.5.
If you look at the difference from SFOS v19.5 to SFOS v20, you finally get more space.
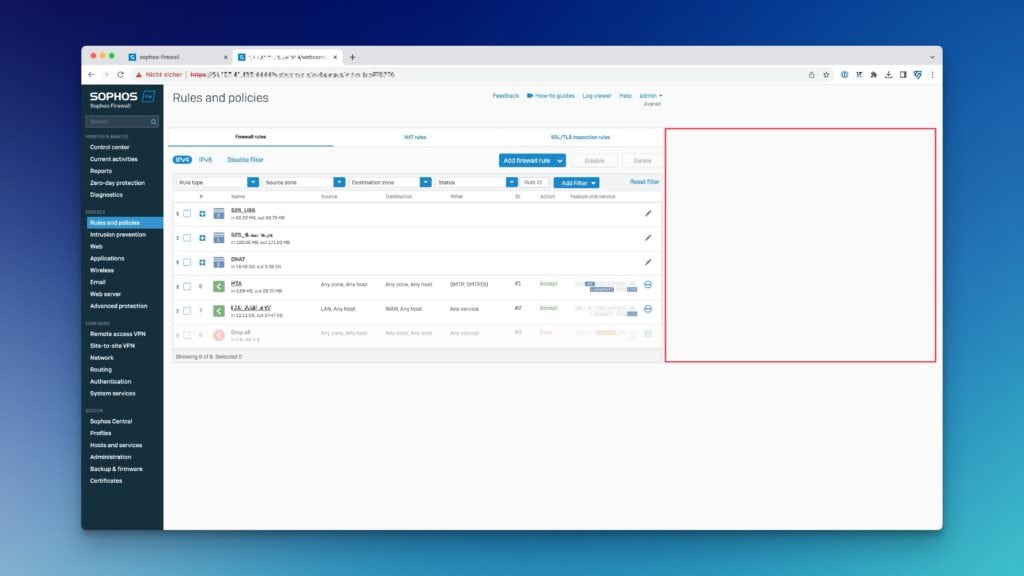
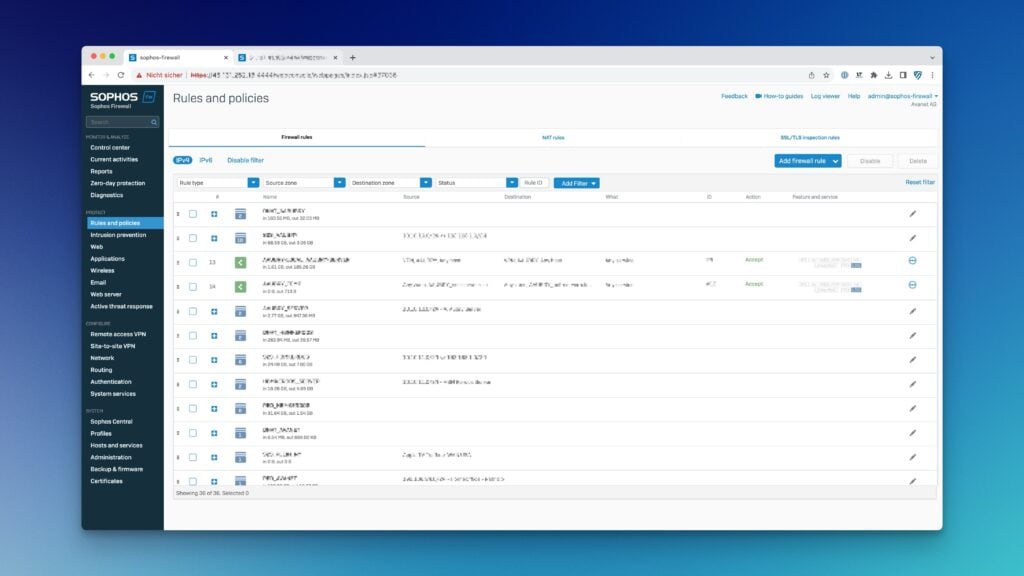
However, the credit here does not belong to Sophos, but to some large Sophos partners who have urged the vendor to implement this. So at this point, thank you very much.
VPN improvements
Sophos Firewall v20 brings various innovations in the area of VPN. Let’s start with probably the biggest change.
VPN portal
With the update to SFOS v20, the VPN functionalities on the User Portal will be transferred to the new VPN Portal. So in the future there will be two portals for the user, provided that the User Portal is actually still used often. But more about that at the end.
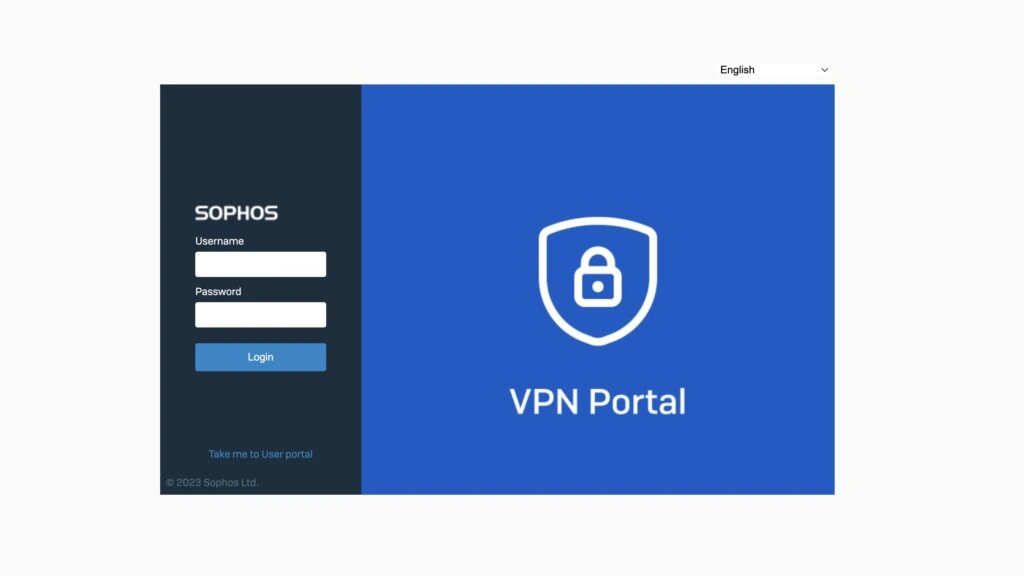
The new VPN Portal in SFOS v20 centralizes VPN-specific functions that were previously in the User Portal.
- Download Sophos Connect Client for Windows and macOS
- Download configuration for Remote SSL VPN and IPsec
- Access to Clientless Bookmarks
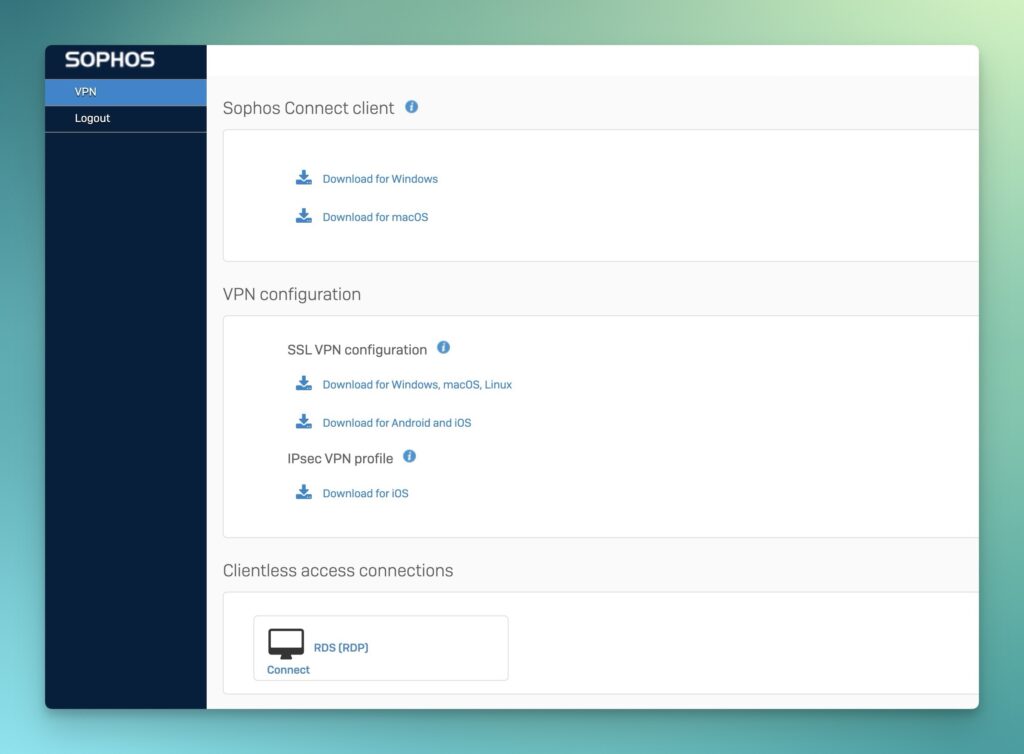
Containerization minimizes access to core SFOS components, making them more secure to use over WAN. Functions regarding authentication methods or MFA remain the same as for the User Portal.
Migration to SFOS 20.0 automatically transfers existing user portal configurations to the VPN portal, making the transition easier. However, there is now a new port for the user portal and the VPN portal runs on the previous port.
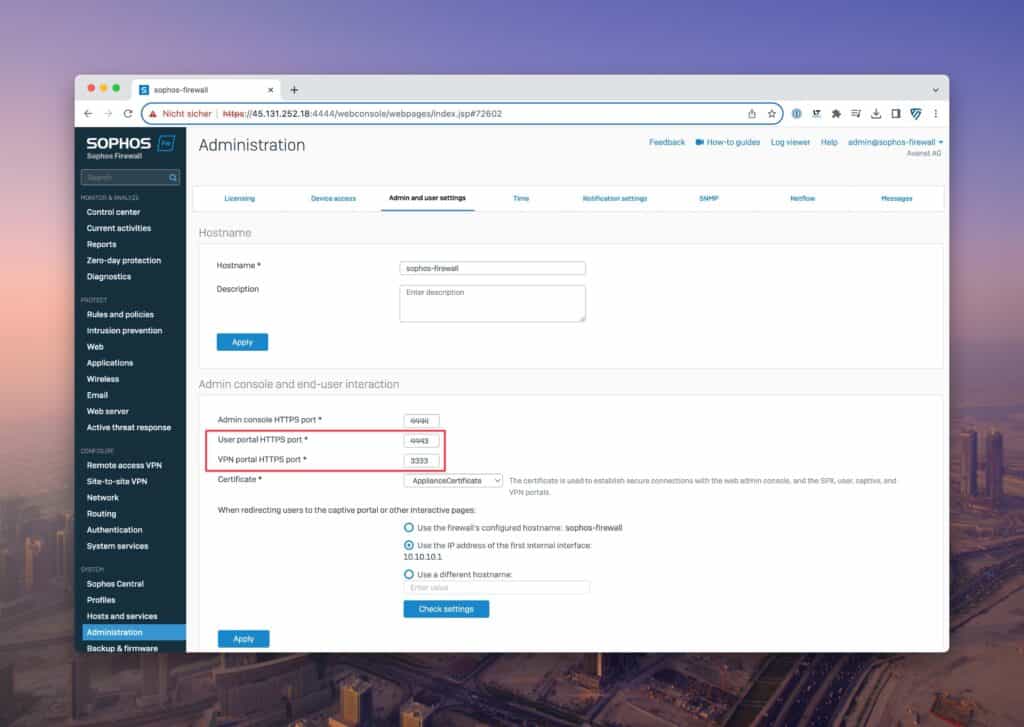
What changes for portals after the update to SFOS v20?
| VPN portal | User Portal |
|---|---|
| Standard port: 443 This means that existing remote access VPN implementations continue to run smoothly. | Default Port: 4443 |
| Port can be shared with the following services: – WAF – SSL VPN | Port cannot be used for any other service. |
| Download: – Sophos Connect Client – IPsec and SSL VPN config – iOS VPN config Guest users do not have access to the VPN Portal. | VPN Client and Configs are now in the VPN Portal. |
| – Auto-provisioning for Sophos Connect Client – VPN configuration pickup via VPN Portal – With default port 443, existing deployments run unchanged | Moved to VPN portal |
| Clientless access to bookmarks | Moved to VPN portal |
| – | – Other client downloads – Internet usage – Email quarantine and exceptions – Exceeding guidelines – Wireless hotspots |
In the Sophos KB you can find more information about this topic: New VPN Portal in SFOS 20.0 and later
So now you can see nicely which functions remain in the User Portal. Looking at the user base for these functions, it is clear that only a very small number of our customers have used them, which means that the User Portal will be used less frequently from now on.
IPsec VPN Stateful HA Failover
Sophos Firewall v20 introduces stateful high availability (HA) failover for IPsec VPN connections. This new feature allows existing IPsec VPN connections to be seamlessly transferred to the standby node in the event of a failover, without interrupting sessions. Here it is important to emphasize which VPN connections benefit from this improvement and which do not.
The improvement affects the following VPN connections:
- IPsec Site-to-Site VPNs (Route Based and Policy Based)
- IPsec remote access VPNs
This means that both remote-access VPNs and site-to-site VPNs can continue in the event of a failover without having to reestablish the connection.
In the context of IPsec VPNs, this feature is particularly useful because it speeds up the recovery of connections in the event of a failover, thereby increasing the resilience of the network. Especially when restoring the connection, problems occurred again and again and VPN connections had to be restored manually or automatically with a certain delay after a failover. This could lead to interruptions in network services, which in turn affected business processes. New you lose at most a few pings, but the connection remains.
With the improvement of stateful HA failover in Sophos Firewall v20, large organizations that rely on high availability can now benefit from increased stability and smooth operation. The new command line options for managing settings also add to the flexibility and control needed when dealing with VPN connections.
Other VPN connections such as SSL VPN and Sophos RED connections are not affected by this particular failover enhancement, but experience has shown that they also work better when connecting.
FQDN Host Support for SSL VPN
In SFOS v20, support for Fully Qualified Domain Names (FQDN) has been added as part of the SSL VPN functionality. With this innovation, SSL VPN connections can now be configured based on domain names instead of just IP addresses. This is especially helpful in dynamic network environments where endpoint IP addresses may change, as changes in network addresses no longer need to be manually updated in the VPN configuration.
FQDN support also facilitates integration with DNS services, which simplifies network name resolution and can improve the overall performance of SSL VPN connections.
Furthermore, FQDN support enables more precise creation of security policies based on domain names, allowing control of network access.
SNMP – Monitor IPsec VPN Tunnel Status
In Sophos Firewall SFOS v20, the feature to monitor the status of IPsec VPN tunnels via Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) has been added. This has also been on our wish list for some time and now simplifies the monitoring of other services.
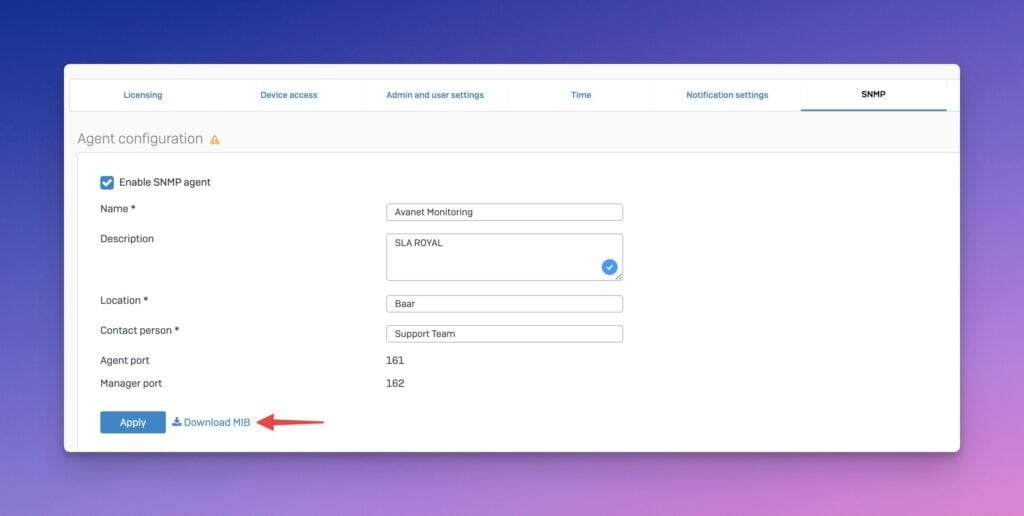
The core component of this feature is the Management Information Base (MIB) file provided by Sophos Firewall. The MIB file is imported into the SNMP tool and provides access to a variety of data points that provide important information about the status, performance, and possible errors of the IPsec VPN tunnels. This allows administrators to perform detailed monitoring and analysis of tunnel activity.
All VPN renewals are explained once again in this video:
Azure AD – Captive Portal SSO & Gruppen Import
Sophos Firewall v20 brings advanced integrations with Azure Active Directory (Azure AD) through two new features: Azure AD SSO for Captive Portal and Azure Group Import and RBAC.
The Azure AD SSO for Captive Portal feature enables users to authenticate to Captive Portal using their Azure AD credentials. This simplifies the authentication process by allowing users to use their existing Azure AD credentials.
The second renewal, Azure Group Import and RBAC, adds a new import assist feature for Azure AD groups and enables automatic promotion for role-based admin changes. With this feature, administrators can easily import Azure AD groups into Sophos Firewall and use them for role-based access control (RBAC). The auto-promotion feature simplifies user role and privilege management by automatically promoting changes in the role-based admin assignment.
The Azure AD extension is progress, but unfortunately we still have to wait for the Azure AD login to be used for the VPN Portal, Remote IPsec VPN or SSL VPN. So we are hoping for updates. 😩
The following video explains the renewal of Azure AD in more detail.
To set up Azure AD on the firewall yourself, these links will help:
Enable / disable interfaces
A long-awaited feature for administrators has been integrated. The activation and deactivation of interfaces. This useful feature was available in the previous Sophos UTM operating system, and SFOS v20 now fulfills administrators’ desire to bring this functionality back.
Previously, an interface could only be completely deactivated, resulting in the loss of the entire configuration.
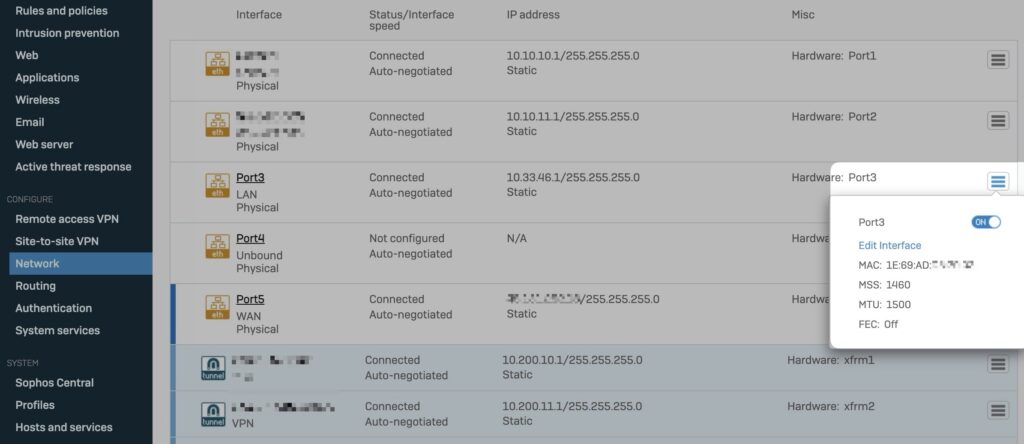
If an interface is now deactivated in the settings, the entire configuration is retained and the interface can easily be reactivated if required.
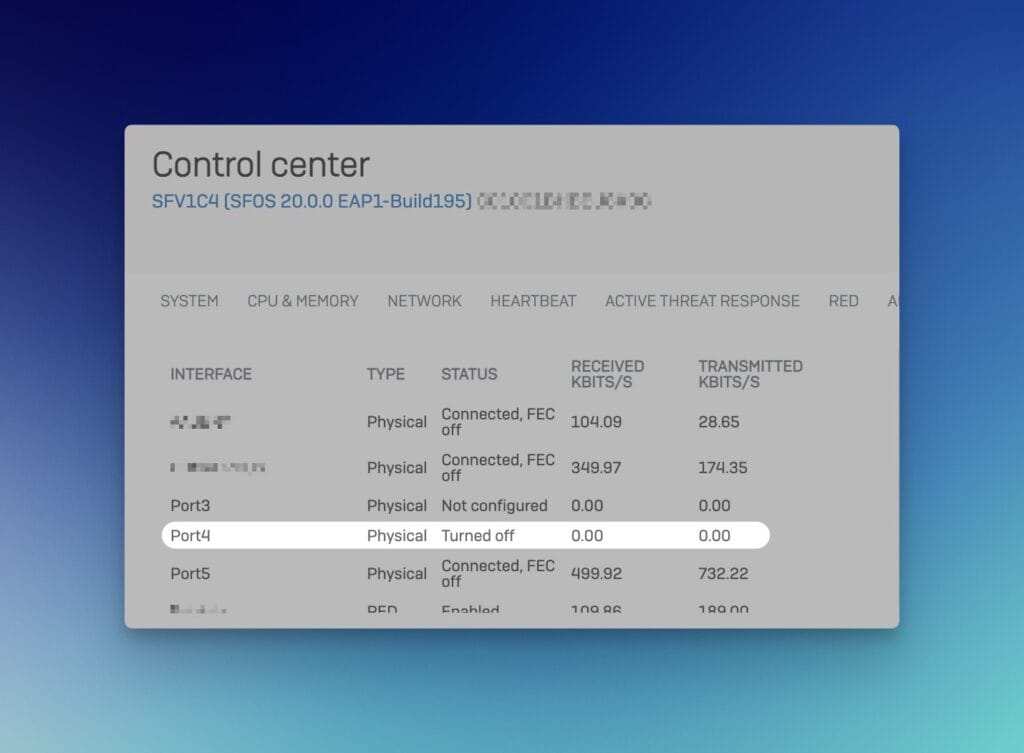
In the disabled state, the line of the interface is grayed out and the status is displayed as Turned off in the Control Center. This enhancement greatly simplifies firewall management and saves administrators valuable time configuring and managing network interfaces.
There are some exceptions where the activation/deactivation of interfaces is not possible. For example, alias or tunnel interfaces or interfaces that are individual members of a LAG (Link Aggregation Group) or bridge cannot be disabled. However, the entire LAG or Bridge interface can be disabled.
| Interface type | Enable/Disable Supported |
|---|---|
| Physical | Yes |
| VLAN | Yes |
| LAG (Group) | Yes |
| LAG individual member | No |
| Bridge | Yes |
| Bridge individual member | No |
| Alias | Planned |
| Wireless LAN | Yes |
| Tunnel Interface (XFRM) | No |
| Wi-Fi | Yes |
| RED | Yes |
Object referencing
The “object referencing” innovation in Sophos Firewall version 20 addresses a previous challenge in managing network objects. In previous versions up to 19.5, it was a tedious task to identify where a specific object was used within the configuration before it could be deleted. This could lead to delays and possible errors, especially in large network environments with a large number of rules and policies.
In version 20 this vulnerability was fixed. In the objects under the“Hosts and services” menu item, all objects are organized in tabs and with SFOS v20, Sophos Firewall shows exactly where this object is in use, be it in a firewall rule, NAT rule, VPN configuration or a service in a group. This facilitates the identification of dependencies and helps to make the necessary changes before the deletion process.
Another powerful feature is the direct link to the rules in which the object is used. With a single click, the administrator can now navigate directly to the rule in question and make the necessary adjustments without spending time manually searching for the rule. This improves efficiency, minimizes error-proneness, and saves valuable time that would otherwise be spent managing and verifying the configuration. Object referencing in Sophos Firewall v20 is thus a significant step towards simplifying administration and preventing configuration errors, which greatly simplifies the daily work of network administrators.
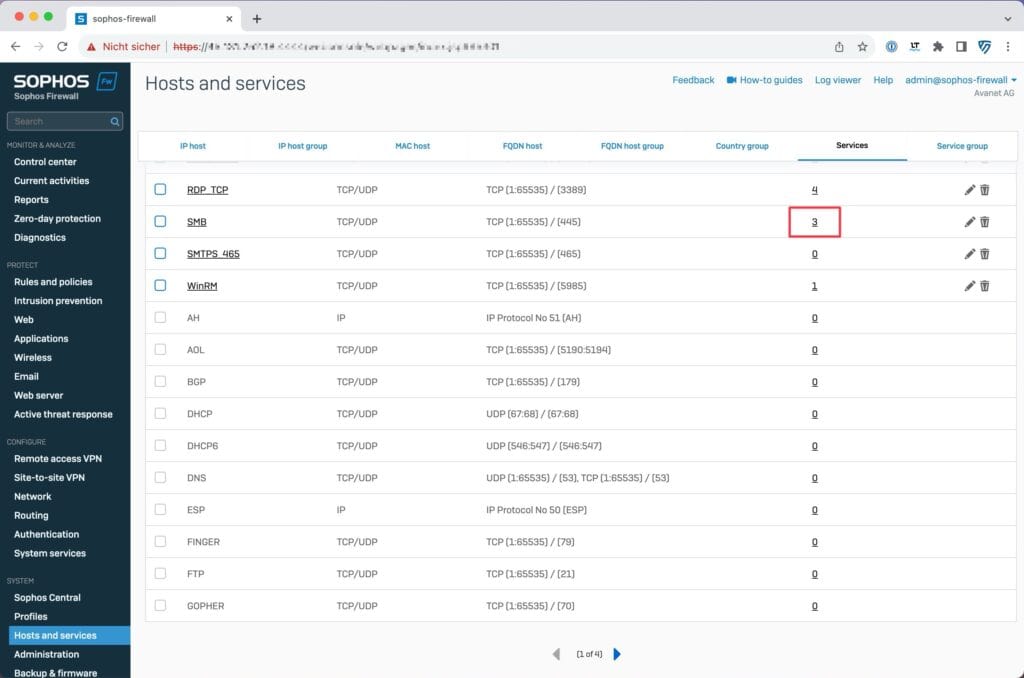
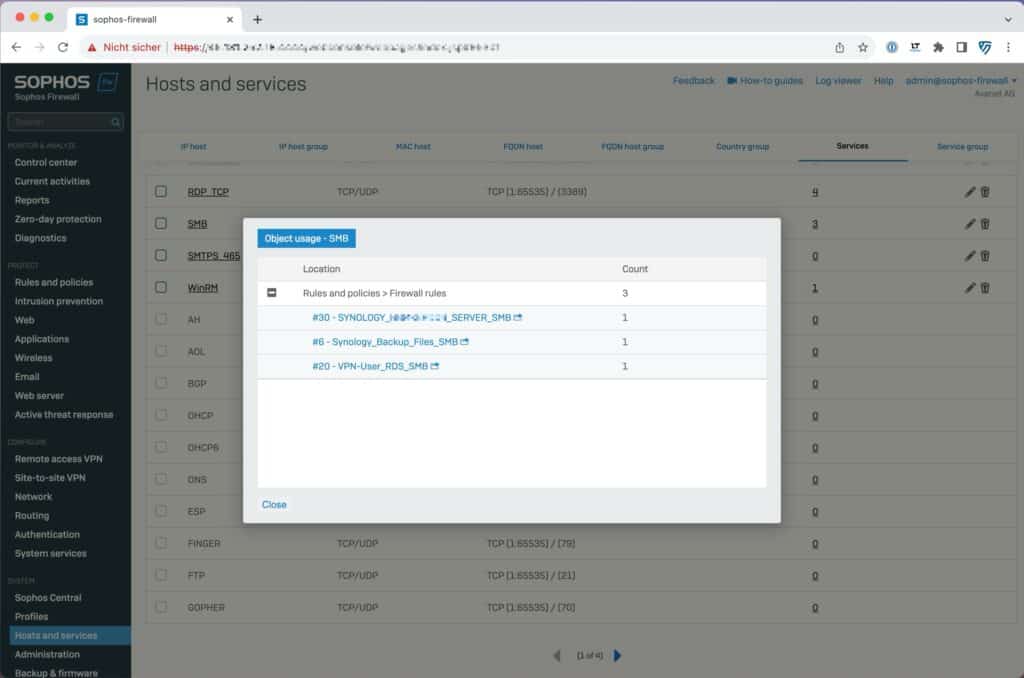
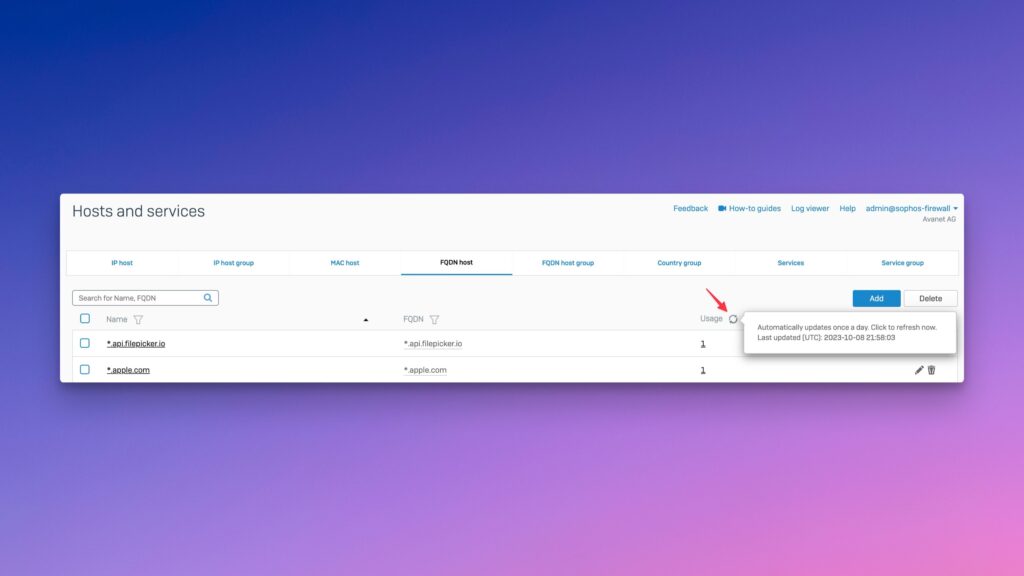
Once per day the referencing is updated, but you can also do this manually.
Sophos itself calls it “Quality of Life Enhancements”. But that’s more like responding to long-awaited customer requests. This video summarizes the improvements once again.
IPv6 Dynamic Routing (BGP)
In Sophos Firewall v20, support for dynamic routing with IPv6 in Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) has been extended. This extension is an important upgrade because BGP is a key routing protocol on the global Internet. Unlike other routing protocols, BGP in SFOS does not require separate processes or services for IPv4 and IPv6, but provides a standardized service that simplifies configuration and management. The user interface has been enhanced so that both IPv4 and IPv6 can be configured on the same page, with separate sections for IPv4 and IPv6 routing information.
In the following video, the renewal in the BGP area is presented once again in detail:
IPv6 DHCP Prefix Delegation
The introduction of DHCP prefix delegation in Sophos Firewall SFOS v20 automates the management of IPv6 addresses. This function allows IPv6 address prefixes to be obtained from the provider and forwarded to the LAN network. When an IPv6 address is received on the WAN interface, it can now be used on the LAN network. A DHCPv6 prefix delegation request to the ISP gives the firewall an IPv6 address range, which is then propagated to the network devices. These receive their globally routable IPv6 addresses through Router Advertisement (RA) messages.
DHCP Prefix Delegation greatly simplifies IPv6 address management and enables smooth adaptation to ISP prefix changes by automatically distributing new prefixes to all connected clients. This improves network efficiency and security, reduces the complexity of manual address management, and promotes more efficient use of IPv6 addresses on the network. This allows certain services to be offered on the network with the received IPv6 addresses from the provider.
The following video explains DHCP prefix delegation again.
Active Threat Response
The following enhancements enable seamless communication between security analysts and Sophos Firewall for proactive response to identified threats.
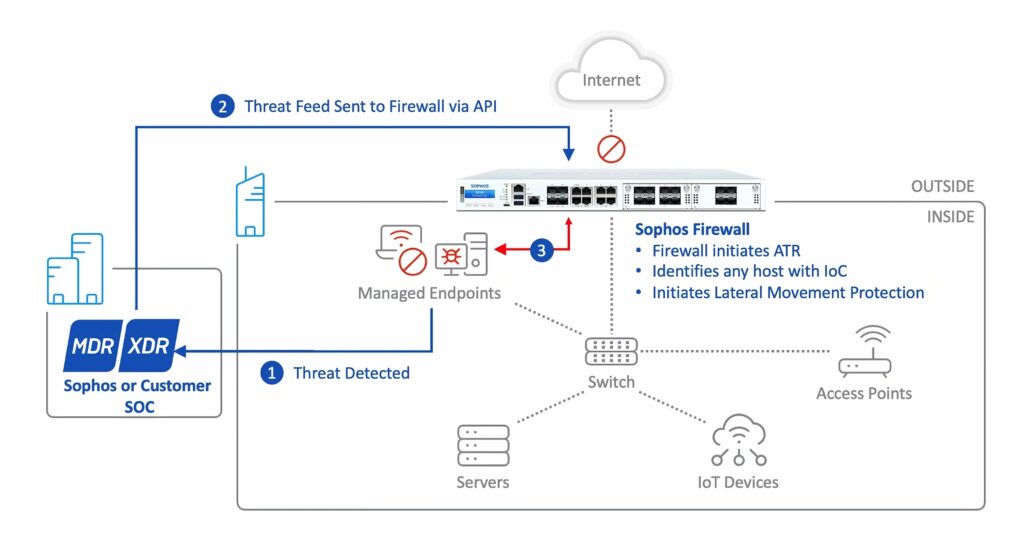
Synchronized Security for MDR & XDR
With Extended Detection and Response (XDR), Sophos Firewall v20 represents a significant advance in automated threat prevention. This feature establishes a direct information link between security analysts and the firewall, enabling a fast and automated response to active threats.
Now threat data can be seamlessly shared with the firewall without the need to manually create firewall rules. This automated information exchange allows the firewall to proactively respond to identified threats and take appropriate defensive actions.
Advantages:
- Reduced manual administration effort
- Increased speed of response to threats
- Improved overall security posture of the network
- Automated response to threats
- Reduced security team time spent on manual configuration and customization of firewall rules
Sophos Firewall v20 adds Managed Detection and Response (MDR) and Extended Detection and Response (XDR) to Synchronized Security. This extension allows security analysts to share active threat data directly with the firewall. A highlight is that the firewall is able to automatically respond to active threats without the need to create separate firewall rules. This further development represents a significant added value, as it significantly reduces the response time to threats and enables proactive protection.
Dynamic Threat Feeds
The introduction of Dynamic Threat Feeds brings a new Threat Feed API framework, which will also be extensible. This feature facilitates the sharing of threat data between the Sophos X-Ops team, other Sophos products such as MDR and XDR, and is expected to integrate third-party threat feeds in the future. This increased flexibility greatly enhances the firewall’s threat intelligence capabilities, allowing for improved threat detection and response.
Synchronized Security
Synchronized Security will be further optimized to enable an even more efficient response to threats identified by MDR/XDR.
A red health status on an endpoint or server usually indicates issues such as active or running malware, malicious network traffic, communication with known malicious hosts, malware that has not been removed, or a Sophos endpoint that is not functioning correctly. In such cases, measures are required to address the security risks.
Automatism (Lateral Movement Protection) on a red health status is now extended to threats to ensure that affected hosts cannot move laterally in the network or communicate externally in the event of a compromise, while key details such as host, user and process are easily accessible for tracking.
The scalability of Synchronized Security has also been optimized to facilitate management in large network environments. False alarms due to missing heartbeats on devices in standby or hibernation mode have been reduced.
New WAF Features
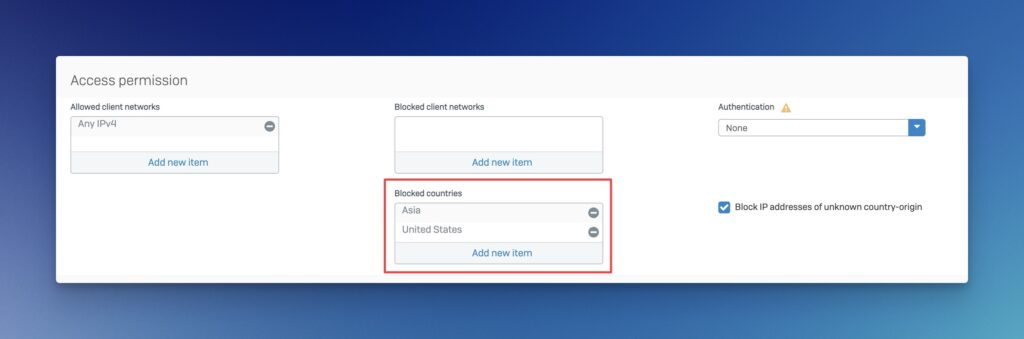
Geo IP control (block countries / regions)
On the Sophos Firewall there is a Geoip ip2country DB which is updated by the pattern updates. In the Firewall and NAT Rules or Local Service ACL Exception Rules, you could already use this. After updating to SFOS v20, it is possible in the Web Application Firewall (WAF) to block access to servers based on geographic location (IP addresses). Users can now block certain countries / regions or continents or allow access only from certain regions. This feature increases security by preventing access from potentially malicious regions, while providing an additional layer of access control.
Cipher configuration
Custom cipher configuration and TLS version settings now allow you to use stronger ciphers (more secure ciphers) and exclude weaker ones. This allows better control over the security of data transmission between users and applications protected by the WAF.
HSTS and X-Content-Type-Options
Improved security through HSTS and X-Content-Type-Options can now implement HTTP Strict Transport Security (HSTS) enforces the use of HTTPS, which improves the security of client browsers. The X-Content-Type-Options setting helps disable MIME type sniffing, which provides additional protection against certain types of attacks.
Third-party SD-WAN integration
Let’s say a company has multiple sites with their own networks that need to be connected to share data and resources efficiently. Instead of the traditional but costly and less flexible MPLS solution, SD-WAN (Software-Defined Wide Area Network) offers a more agile and cost-effective alternative.
With third-party SD-WAN integration in Sophos Firewall v20, traffic can be seamlessly transferred to the high-performance backbone networks of Cloudflare, Akamai or Azure. For example, an organization that needs faster and more secure connectivity between its sites can route traffic over the Azure backbone network to benefit from its global reach and robust security services. This improves performance, security and reliability while reducing network complexity and cost.
Onramping to backbone networks from providers such as Cloudflare, Akamai or Azure creates a bridge between the local network and the extensive network infrastructures of these providers. The integration of third-party SD-WAN solutions in Sophos Firewall v20 simplifies this process.
ZTNA Gateway
This feature is not new per se, as it was already integrated into the firewall with SFOS 19.5 MR3, yet Sophos lists it again among the new features in SFOS v20.

The article on this topic can be found here: Sophos ZTNA Gateway on Sophos Firewall








